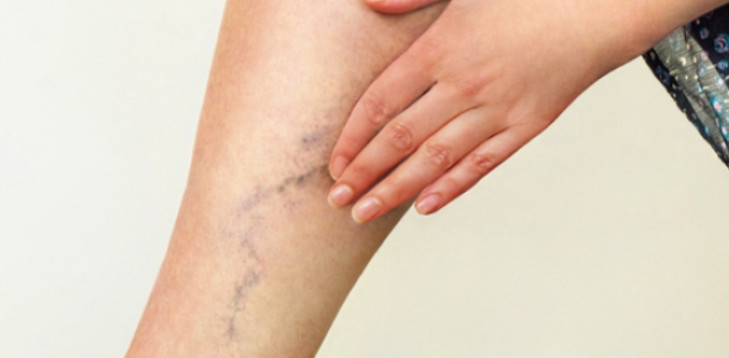
Symptoms of venous insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral).
The following features are indicative of venous insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral) disease
Today We writting best treatment for Venous insufficiency
- Vein ulceration
- varicose veins
- Hyperpigmentation
- Chronic leg formula
- Chronic ankle sprains
- Phlebitic lymphedema
Venous insufficiency (chronic) is a common cause of (peripheral) disease
The most common causes of venous insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral) are as follows:
- Blood clots in deep vein blood vessels
- Arterial flow
- Superficial vein thrombosis
- May-Thurner syndrome
- thrombophilia
- arteriovenous fistula
Risk factors for venous insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral) disease
The following factors increase the risk of developing venous insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral) disease:
- family history
- obesity
- tall height
- female
- sitting for long periods of time
- Long lasting
- pregnancy
- History of deep vein thrombosis of the legs
Prevention of venous insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral) disease
Yes, it may be possible to prevent (chronic) (peripheral) venous insufficiency. This disease can be prevented by following steps:
- Manual Compression Lymphatic Massage Therapy
- Skin lubrication
- Ankle pump exercise
- Use of blood pressure medication
- Rest of the leg by elevating the upper heart level
- Hold the Trendelenburg position
Incidence of Venetian insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral).
This disease is more common in men of that sex
- People of either sex can develop (chronic) (peripheral) venous insufficiency
- Tests to detect Venous insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral) disease
- The following tests are done to diagnose Venous insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral) disease:
- Ultrasound examination: to see the valves in the veins sucking blood
- Physical examination: To check for leg swelling
Complications that can result from untreated venous insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral) disease
Yes, Venous Insufficiency (Chronic) (Peripheral) can cause physical complications if left untreated Below is a list of complications and problems that can occur from untreated Venous Insufficiency (Chronic) (Peripheral):
- Very painful ulcers
- thrombophlebitis
- war victims
- fatality
Treatment steps for Venous insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral) disease
The following steps are followed to treat Venous insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral) disease:
- Sclerotherapy: treatment of varicose veins in severe cases
- Laser surgery: closure of small varicose veins and spider veins
- High blood pressure and vein stripping: Close off varicose veins to prevent blood flow
- Ambulatory Phlebectomy: Varicose Vein Treatment
- Endoscopic vein surgery: treatment of varicose veins in advanced cases
Do-it-yourself service for Venetian insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral).
Following is a list of self-care or lifestyle changes that may be helpful in treating or managing Venous insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral):
- Regular exercise: Helps reduce the discomfort that varicose veins can cause
- Maintain a healthy weight: Helps reduce the abnormalities that varicose veins can cause
- Eat a healthy diet: Helps reduce the discomfort that varicose veins can cause
- Avoid high heels: helps treat varicose veins and find best shoe for Venous insufficiency
- Stretch your legs: Helps improve leg circulation
- Avoid long periods of sitting or standing: Helps improve circulation in the legs
- Don’t sit with your legs crossed: Helps reduce blood circulation problems
Alternative medicine for the treatment of Venous insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral) disease
Some alternative medications and therapies that may be helpful in treating or managing venous insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral) include:
- Dietary butcher’s shower supplement: Helps treat chronic venous insufficiency
- Use horse chestnut supplements: Helps treat chronic venous insufficiency
- Use sweet clover supplements: Helps treat chronic venous insufficiency
During the treatment of Venous insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral) disease
Although the time-frame of treatment varies for different patients, if properly treated under the supervision of a specialist, the time-frame for venous insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral) disease to come under control is as follows:
- 1 – 4 week
Read More Airticle



